[credit]
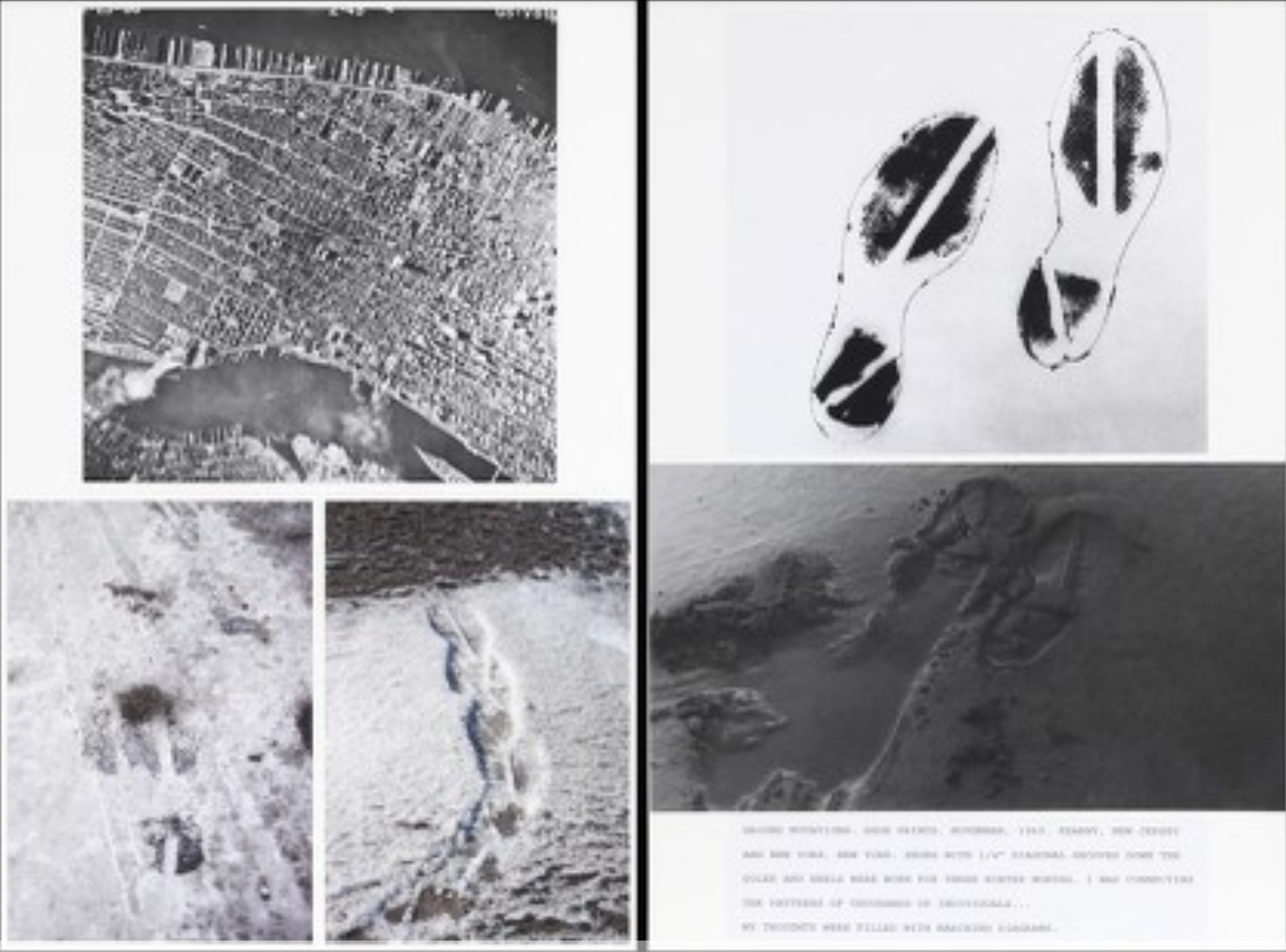
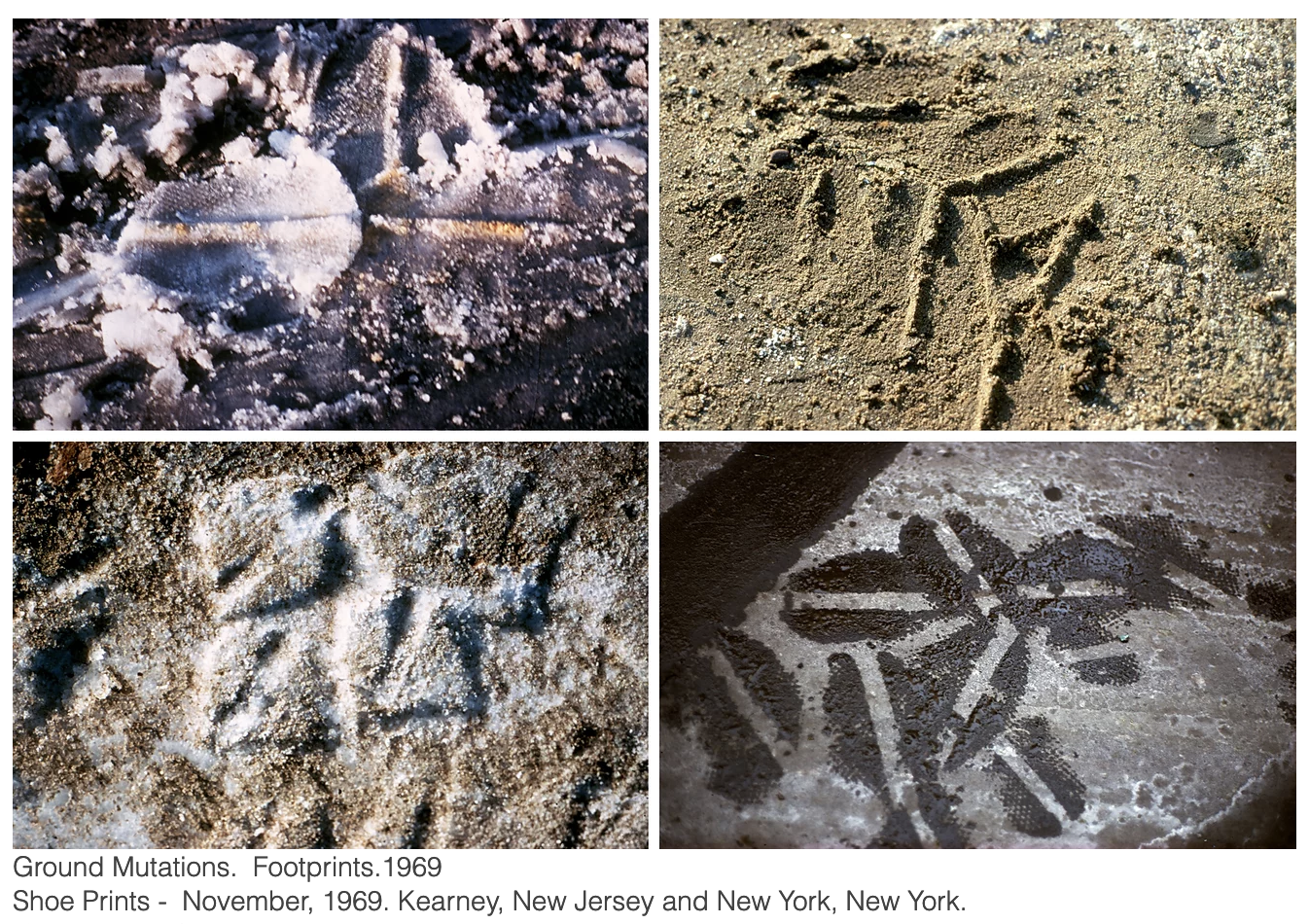
Ground Mutations – Shoe Prints, November 1969, printed 2013
Black-and-white and color photographs and text on two panels

[credit]

[credit]
Black-and-white and color photographs and text on two panels

[credit]
A more recent walking artwork highlighting the intersection of walking and race is In Between Camps (2012), which consisted of a group of six researchers and artists, Ismael Al-bis, Fabio Franz, Matteo Guidi, Thayer Hastings, Ibrahim Jawabreh, Saleh Khannah, Sara Pelligrini, Giuliana Racco, and Diego Segatto, walking across the West Bank from the springs of al-Arroub to Solomon’s Pools (three massive stone reservoirs) south of Bethlehem in search of an ancient Roman waterway, the Arrub Aqueduct. The project originated from the Campus in Camps program developed by Al-Quds University, an experimental education program in the Palestinian refugee camp of al-Dheisheh. The purpose of the project was to both reactivate the water system’s source, and imagine a time-frame before the contemporary apartheid-reality of walls, colonial land parceling, and occupation of Palestine. While they were hiking, the group was stopped by Israeli soldiers who were suspicious of the Palestinian participants due to their skin tone and dress. The international participants intervened and explained the trip, their search of the aqueduct, and showed them the map, engaging in a type of information overload tactic, not unlike the tactics Codogan described for minimizing the perception of criminality. After the walk, the group created a booklet (Booklet ) reflecting on the history of the site, their experience, and how the various layers of race-based rule and exclusion are projected on the land.
—
Hastings, Thayer. “Tracing a Line Through a Fractured Palestine, from al-Arroub to Bethlehem,” Walking Art / Walking Aesthetics. Accessed May 16, 2022: https://walkingart.interartive.org/2018/12/thayer-palestine
“Six photographs of unremarkable industrial landscapes in Passaic, New Jersey depict evidence of man-made history, yet the title of “monument” seems ironic. Stripped of any apparent artistic agenda, the images appear photojournalistic—without an accompanying news article to inform our perception. Smithson was perpetually intrigued by suburbia; in its sameness he saw a version of eternity defined by formal repetition rather than temporal longevity. By framing the mundane sites as “monuments,” Smithson challenges the conceptions of aesthetic merit and historical significance. Monuments of Passaic exists as three manifestations: a published article in Artforum, a photowork, and a photographic series.” [credit]
Robert Smithson – A Tour of the Monuments of Passaic (PDF)
He drew further attention to site-specificity and the passage of time via his walk along the river and industrial sites.
Was installed outside the Menil Collection in Houston, Texas, United States.
Image 2: Photo: Tom Vinetz Image 3: Photo: Tom Vinetz

“The first version of this work was the ninth of the artist Michael Heizer’s “Nine Nevada Depressions” made around the state in 1968. This one is a circular loop made in a dry lake bed surface, at Massacre Dry Lake, near Vyo, Nevada. Six tons of earth was displaced, making a one foot wide trench, around 120 feet long, with the loop being 12 feet in diameter. Commissioned by Robert Scull. Apparently, no traces remain.” [credit]
Reg Carremans (1981-) is a Brussels-based visual artist mapping the self and the environment through different media, to encourage critical introspection, (self-)awareness and reflective thought. Interested in humans as geographical beings (walking, landscape, environment, place, territory, cartography), and the artist and artistic processes (identity, basic actions, economy).
“Pathscape is a canvas walk for Sideways, a month-long itinerant initiative for contemporary art and culture. August – September 2012 | Belgium | Walks, canvas patchwork” [credit]
—
“Reg Carremans is a landscape painter who makes his work through walking or rubbing against the environment in which he is in. He was the only Belgian artist to complete the 375km Sideways 2012 Walking and Art Festival route, using canvas on the soles of specially adapted walking boots to gather multiple impressions for a series of ‘landscape paintings’ displayed en route.” [credit]
“Beginning in 2007, started photographing along the U.S.-Mexico border between El Paso/Juarez and San Diego/Tijuana. My project is organized around an effort to document all of the monuments that mark the international boundary west of the Rio Grande. The rigorous undertaking to reach all of the 276 obelisks, most of which were installed between the years 1891 and 1895, has inevitably led to encounters with migrants, smugglers, the Border Patrol, minutemen and residents of the borderlands.
During the period of my work the United States Border Patrol has doubled in size and the federal government has constructed over 600 miles of pedestrian fencing and vehicle barrier. With apparatus that range from simple tire drags (that erase foot prints allowing fresh evidence of crossing to be more readily identified) to seismic sensors (that detect the passage of people on foot or in a vehicle) the border is under constant surveillance. To date the Border Patrol has attained “operational control” in many areas, however people and drugs continue to cross. Much of that traffic occurs in the most remote, rugged areas of the southwest deserts.
My travels along the border have been done both alone and in the company of agents. In total, the resulting pictures are intended to offer a view into locations and situations that we generally do not access and portray a highly complex physical, social and political topography during a period of dramatic change.” [credit]
“Lickable Cities is a research project that responds to the recent and overwhelming abundance of non-calls for gustatory exploration of urban spaces. In this paper, we share experiences from nearly three years of nonrepresentational, absurdist, and impractical research. During that time, we licked hundreds of surfaces, infrastructures, and interfaces in cities around the world. We encountered many challenges from thinking with, designing for, and interfacing through taste, including: how can and should we grapple with contamination?, and how might lickable interfaces influence more-than-humans? We discuss these challenges to compassionately question the existing framework for designing with taste in [Human-Computer Interaction].” [credit]
Chain Link Maze, 1978-79 (destroyed), Galvanized chain link fencing, 8′ x 61′ x 61′, University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
—
“Adjacent to the University of Massachusetts football stadium in Amherst stands an 8-foot-tall chain-link fence encompassing an area some 60 feet square [by Richard Fleischner (1944-)]. …
The work sits, as do most of Fleischner’s projects, delicately on its terrain—it does not so much structure the natural, open site as it asserts itself discreetly, sensitively on the slightly rolling topography as a neat, geometrically concise object. Once through the corner entryway, we are confronted with a long corridor, the beginning of a path that winds, multicursal, toward a central inner chamber. Decisions must be made, and confusion is possible as we look through the wire grid at spaces beyond our reach. Both entry and path are ample, affording no sense of claustrophobia. One is struck instead by the open, hospitable feeling of the first corridors as they trace the perimeter. Comfortable strides are possible within the labyrinth; one can even turn or stop easily. It is not long before one of several decision points is reached—several paths can be taken but no great mistake can be made. It is as if the artist wants to coax us gently through this experience. There is no threat here but instead a fuller, more rewarding task of finding one’s own way. We are separated spatially but never visually from the outdoor environment as we can almost always see shimmering details through the various layers of mesh.
As one traverses the walkway, patterns of light reflect off the metallic walls, sometimes creating moiré-like surfaces, at others seeming almost flat and mat-colored. Fleischner has given us a visual labyrinth as well as a participatory maze. In no other maze are almost all the parts visible even as we are confined to a specific track. Depending on how many layers of chain link we gaze through (and this can vary from one to almost a dozen), details of the environment and other figures in the maze fade in and out of our sight. This seems then the perfect visual accompaniment to the fugitive spatial experiences we all undergo within a labyrinth.
In Chain Link Maze, Fleischner uses intuition to achieve his means—physical, optical and psychological experiences that depend on carefully measured spaces. In a broader context, a work like this directly engages some of the notions, particularly American, of the unbounded, natural environment. Fleischner works directly in the landscape, sometimes using concepts from rarified historical traditions. He has reasserted his ability visually to grasp the given landscape in a particularly American fashion, while simultaneously structuring situations within that landscape derived from conventions of garden design, architectural history and spatial perception. —Ronald J. Onorato ” [credit]
“Fissures, Holes, Limbs: breathing dislocated scales is an eco somatic sound walk centering disability.
I-Park Kicks off Seventh Art Biennale in East Haddam
BY CATE HEWITT, SEPTEMBER 23, 2019 ART & DESIGN
EAST HADDAM — At night, animals, birds, flowers, and even mushroom spores become active, moving about, making sounds and leaving traces, mostly unbeknownst to humans.
Participants in artist Moira Williams’ sound walk called “Fissures, Holes, Limbs: breathing dislocated scales,” were invited Sunday to shift from “daylight to moonlight” and experience night sounds and images she had recorded onsite at I-Park, an international artist-in-residence program founded in 2001.
Williams, a New-York-City-based artist, is one of nine artists in I-Park’s seventh Site-Responsive Art Biennale who spent three weeks on the program’s 450-acre campus “creating ephemeral artworks that respond to the property’s natural and built environments,” according to the program notes. The artists’ works can “take the form of environmental sculptures, videos, aural experiences or performance pieces.”
At the beginning of Williams’ sound walk, participants were asked to choose a stick from a number of precut tree branches, mostly about five or six feet in length. These branches were used as “limbs,” extensions of the human body, to explore holes and fissures in the path, as well as rocks and lichen.
After the band of sound walkers set off along a path, Williams stopped the group at a field and played a recording she had made while camping onsite of an owl hooting.
“Think of how the owl moves so quietly throughout the night and what it disturbs and what it accentuates, think of the different way our breath moves and accentuates as well, think of the spores and the seeds that we never see that we move,” she said.
She asked the group to face the field and to lift up their shoulders and think about them as wings, with the limb as an extension of sorts.
“Think about how they feel in the air and what you can move and what you can share and extend,” she said. “If you have a limb, an extra limb with you, please raise your limb in any way that you like, and think of your shoulders and your extra limb, think of the breeze going through your shoulders and your extra limb.”
Dressed in a white hazmat-type suit embellished with bright neon stripes made from tape, Williams carried a roll of black wire on one shoulder, like a techie epaulet, and a small speaker and projector connected to her mobile phone in a pouch around her waist. On her head was a wide “hat,” made from a piece of flat white painted cardboard with a space cut out for the top of her head, and long neon green streamers attached at each end that trailed behind her when she walked.
As the group proceeded down the path, Williams removed her hat and projected a tiny video of a fox she had recorded at night, letting the walkers experience the sight and sound as they hiked past.
She asked everyone with “an extra limb” to use it to touch the rocks, holes and lichen along the path, as a way to experience the site.
Soon the group came upon a field where Williams had created a labyrinth.
“Choose a path and walk to where you can find a white stump,” she instructed. “We’re under a full moon in the middle of the night, it’s an extraordinary full moon.”
Soon the group gathered around a white stump that had holes drilled in it about the size of the limb walking sticks. She asked those who had limbs to share them with those who were without.
“Those who haven’t had an extra limb, think of the limb that they now have and how the previous person used that limb and what that means to them not to have it now,” she said. “And think about whether the bark is smooth and whether there’s holes or fissures or lichen or even insects on your limb.”
Williams invited everyone holding a limb to place it in one of the holes in the stump, which created a kind of tree sculpture. The new tree symbolized connection, she said, and could forge a new identity for everyone who took part.
“If you walked with an extra limb and want to think about if you have a new name, you can say your new name out loud if you do have one, or if you can think of a new name that might incorporate an extended limb,” she told the group. “My new name would be Lichen.”
Of the 20 participants, names like Woody, Meadow, Shaggy, Hiawatha and Tripod emerged.
Then Williams directed the walkers’ attention to the far side of the meadow where a large tree with bare branches reached to the sky, a living reflection of the group’s tree made from limbs.
“Look at the tree in front of us and think about the tree behind us and the juncture of all of us connecting all of us,” she said.
Williams next led the group to a boardwalk that snaked through a marshy area with numerous streams flowing along the ground.
At one point she stepped out of the path and projected a video of mushrooms sporing onto a series of white vertical boards that were set in the marsh.
“This is an image of sporing mushrooms that only spore at night and these are things we seldom get to see,” she said. “They’re just ghostlike spores that we’re gathering on our own bodies and sharing with the rest of the world.”
Williams, who holds a BFA from the School of Visual Arts, a graduate certificate in “Spatial Politics,” and an MFA from Stony Brook University, said her underlying interest is about “making the environment accessible to all people, especially people with disabilities.
“It’s about thinking in ways that are not about independence but more about connectedness with the environment and one another,” she said. “It’s connectedness as a holistic ecosystem, we’re not just this very big myth about how we’re independent.”
She explained that her white outfit reflects a philosophy of healthcare — “the idea of nursing and empathy and being a caregiver.”
“I think of myself as a steward caregiver. I love wearing the white suit because I’m in the lead and I want people to see me,” she said. “The hat is a device to say, hey, here I am, come and join me, but it’s also the width of walkways that need to be for people that need a wheelchair.”
By walking through the marsh and the woods, participants will carry traces of the environment to new places, she said.
Near the end of the path, Williams crouched down, removed her hat and projected a time-lapse video of a lotus flower opening and closing at night on the pond at I-Park, a film she made while floating on the water.
The tour was over and she bade the group good-bye by saying, “Good morning everybody.””
“Heath Bunting emerged from the 1980s art scene committed to building open, democratic communications systems and social contexts. Throughout his career, he has explored multiple media including graffiti and performance art and has staged numerous interventionist projects, as well as being a pioneer in the field of Internet Art. Bunting began collaborating with artist Kyle Brandon in 2001.” [credit]
These artists devised a circular tour (see map), and by night stealthily cut some fences as part of their Borderxing project. BorderXing serves as a pratical guide to crossing major international borders, legally or illegally. It was a type of physical hacking of space, cutting anything that impeded their walk – D’Fence Cuts. Below is an excerpt from their tour de fence catalog:
“tour de fence is the answer to your real needs. while the internet promised to level out all barriers, tour de fence enables you to surmount the fences out there that people erect to obstruct your way every day. from wire netting to ru stic fence, from steel door to close security system, tour de fence offers you the necessary know-how for unhampered movement. tour de fence is the direct way.
learn offroad mobility within high security architecture. cross over stretches of land in the right direction. penetrate the underground area of your city. tour de fence puts an end to the relocation of your movements into virtual space. use the tour de fence! become a tour de fence amateur team. pass this handbook on to others. propagate tour de fence.
by doing so you will become part of the international tour de fence community. as a reader, a free-climber or by sending one of the 24 tour de fence postcard in this book.
participate now! tour de fence’s vision is to do what we want.
…
tour de fence acknowledges fence as metaphor for private property. fence as a supposedly temporary, often mobile barrier performing functions of inclusion and exclusion, entrapment and guided freedom, decoration, safety, user boun dary, protection from hazard, flow control, visual screening and user separation.
fence is a permeable filter system defining permitted use and users. light, wind, insects, water, plants and sound pass unhindered while high order life forms such as·humans, fish, cattle and cars are engaged:
development of fence.
up to now the vertical has generally been private while the horizontal public. increasingly, vertical fences are being rotated to the horizontal and enlarged over large areas of land, as all use and users are embraced in total control.
tour de fence recognises the transformation of framed freedom into restricted open-range roaming; the re-alignment of unknown possibilities into known re peatables. users are permitted to skate across flattened surface of fence, but not to pass through – the fence is everywhere.” (credit)