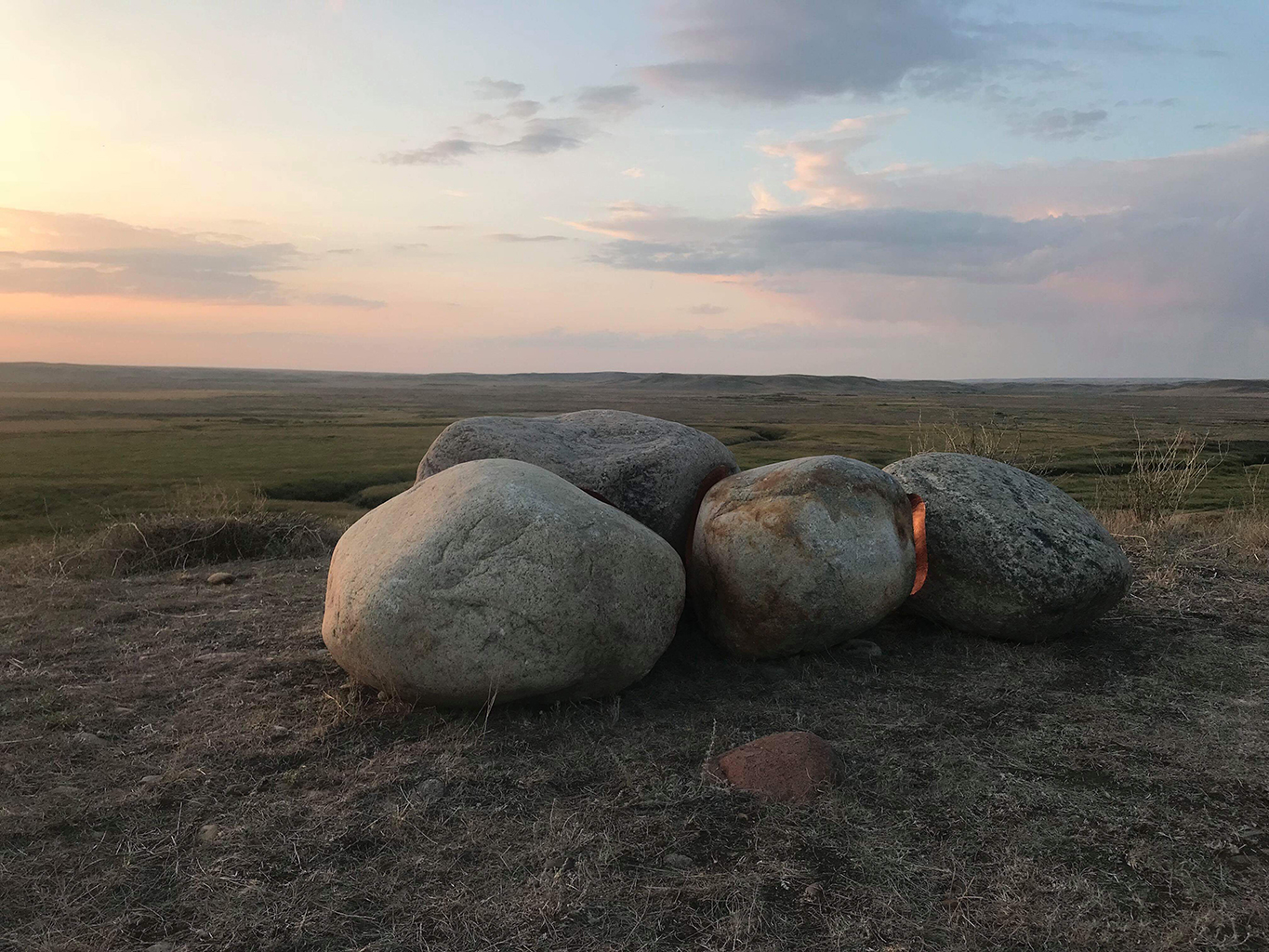
Ban Abidi, “Security Barriers A-Z” – type A – Iranian Embassy, Shahrah-e-Iran, Clifton, Karachi (CREDIT)
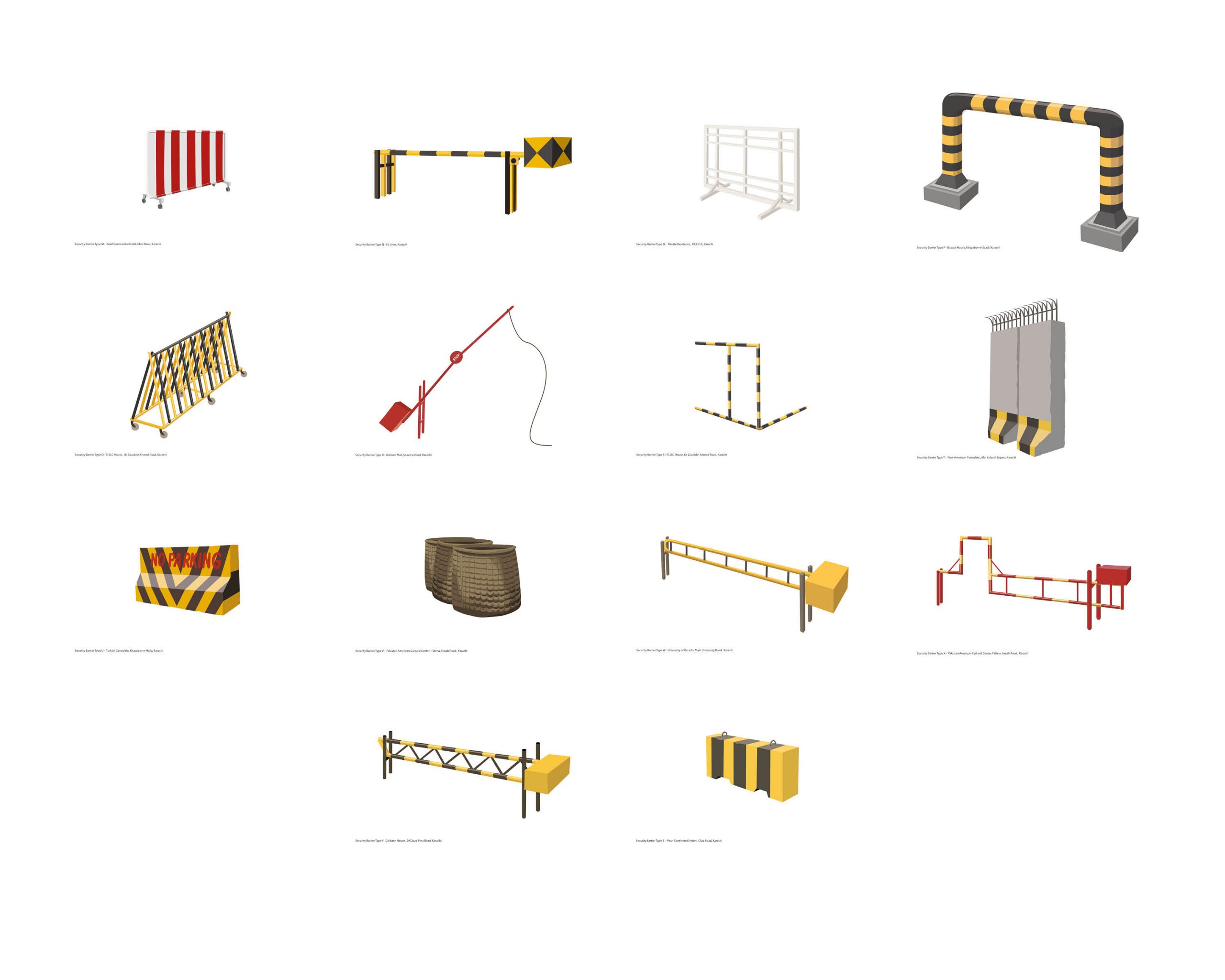
Bani Abidi, Security Barriers A-Z (selection of M-Z; 2019) [CREDIT]

(credit)
Bani Abidi, (1971-) in Karachi (PK), lives and works in Karachi and Delhi (IN)
“26 Inkjet Prints, 29.7 x 42.0cm
A design typology of security barriers found on the streets of Karachi (2009 – 2019). These barriers, which started making an entry into Karachi’s streets soon after the attack on the Twin Towers in NY in September 2001, raise questions around the notion of safety and economic segregation, state control and political strategies of demarcation. Out of context, against a white background, they resemble minimalist abstractions.” [credit]
—
“Security Barriers A-L, 2008
The artist Bani Abidi is a nomad of two cultures. Born and brought up in Karachi, Pakistan, she lives and works today in Delhi, India. These biographical details run through her humorous works that depict the cultural and political differences and similarities between the two countries and their conflict-ridden border. In her work Security Barriers A-L, Abidi employs temporary architectural elements for an analysis of political manifestations of state violence, the maintenance of state power, and national strategies of demarcation.
In twelve prints, the artist catalogs the various models of security barriers in her hometown of Karachi, which she first photographed on-site, before going on to digitally rework them. She found the various constructions in front of embassies, consulates, at airports and intersections. Arranged in rows of three, the brightly colored, clear, and sharply contoured vector drawings against a white background are like objects featuring in a glossy catalog. One almost feels tempted to order one of these beautiful objects for the front yard, even though their design idiom is unambiguously that of a barrier. Only the attached titles establish the link to their original context and the related strategies of isolation and demarcation: type H stands out among the drawings with its all too vigorous expression of political superiority, while the flower-bedecked barrier in front of the British Deputy High Commission of the former colony almost seems smarmy. (KB) [credit]”
—
“Bani Abidi’s early engagement with video, beginning at the Art Institute, led to the incorporation of performance and photography into her work. These mediums have provided Abidi with potent, sometimes subversive means to address problems of nationalism—specifically those surrounding the Indian-Pakistani conflict and the violent legacy of the 1947 partition dividing the two countries—and their uneven representation in the mass media. She is particularly interested in how these issues affect everyday life and individual experience.” (credit)
—
“…It is the life of ordinary citizens that interests Abidi—not the heroic tale, but the poetry of the quotidian struggle for freedom of those who die laughing, or defiantly laugh in the face of death….
…
I want to make a strong point about the fact that my work is not about Pakistan. It’s about power, security, and militarised architecture; and it’s about the vulnerability of regular people.
We ought to be aware and assert the fact that such an identity-based reading of culture only happens when a work by a brown person is shown in a white space. A romance set in Paris is never perceived as being ‘about’ France, is it? What you see in my films is what I know and assume as my normative: the sounds, smells, landscape, and temperature . . . these are the details that help tell a story.
I am certainly not out to teach anyone anything about my country. My practice draws from a large spectrum of present and past experiences, and I hope to be able to speak to anyone who is interested in those ideas.
Of course, there are many layers in my work and its reading very much depends on the context in which it is placed….” (credit)








