“he scrapes and smears dozens of layers of paint across massive canvases using a giant squeegee.” [credit]

“he scrapes and smears dozens of layers of paint across massive canvases using a giant squeegee.” [credit]

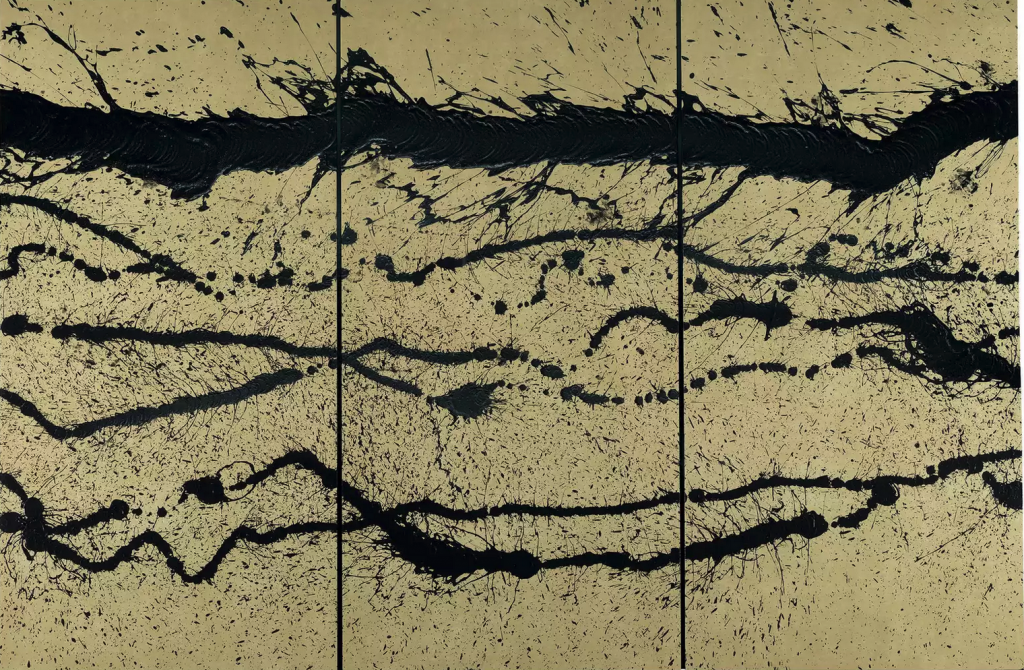
“Helen Frankenthaler (Dec. 12, 1928 – Dec. 27, 2011) was one of America’s greatest artists. She was also one of the few women able to establish a successful art career despite the dominance of men in the field at the time, emerging as one of the leading painters during the period of Abstract Expressionism. She was considered to be part of the second wave of that movement, following on the heels of artists such as Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning. She graduated from Bennington College, was well-educated and well-supported in her artistic endeavors, and was fearless in experimenting with new techniques and approaches to art-making. Influenced by Jackson Pollock and other Abstract Expressionists upon moving to NYC, she developed a unique method of painting, the soak-stain technique, in order to create her color field paintings, which were a major influence on such other color-field painters as Morris Louis and Kenneth Noland.
One of her many notable quotes was, “There are no rules. That is how art is born, how breakthroughs happen. Go against the rules or ignore the rules. That is what invention is about.”” [credit]
Acrylic and mixed media on canvas, 70 9/10 × 107 1/10 in credit
“Standing on the canvas that covers a majority of the studio floor, the artist grips the bicycle-like handlebars to move the enormous paintbrush, suspended from the ceiling and carrying up to 68 litres of paint.
As her unique method proves, Fabienne Verdier is no conventional painter. Yearning to “master the notion of spontaneity in painting” and dissatisfied with the arts education available in her native France, Verdier moved to China in 1984, at the age of 22, to study at the Sichuan Fine Arts Institute. “I was fascinated by the illustrations of the works by Chinese painting masters,” she recalls. “The purity and incredible dynamism of the lines, and the spiritual freedom exuded from them propelled me to leave for China.”
For 10 years, Verdier studied under master calligraphers and painters, including her late mentor Master Huang Yuan, who taught her to discover a new form of abstraction via Chinese calligraphy. “My Western aesthetic knowledge was totally put to question,” she says.
Now based back in France, Verdier is one of the only Western artists known for employing a Chinese medium in her art, and to great success. Her massive abstract paintings —made with the extraordinary method chronicled in the acclaimed documentary Painting the Moment—can command hundreds of thousands of dollars. In addition to solo exhibitions throughout Europe and Asia, Verdier’s work is also part of the collections owned by institutions such as the Centre Pompidou and the Foundation François Pinault in Paris, and the Chinese Ministry of Culture in Beijing.
Both French and Chinese, traditional and modern, spontaneous and planned—her work itself is a dialogue about the dichotomies inherent in life. “We have within us both rationalism and intuition; we are torn between analytical rigour and total spontaneity; divided between a necessity to calculate and to imagine without constraint,” she explains. “From these apparent contradictions come energy and the meaning of life itself. It is this tension that runs through all of us that I aim to explore in my work.”
For “Now and Then: Reflections on Contemporary Ink,” the show presented by Art Plural Gallery in Singapore this month, Verdier created six new works in which she aimed to “invent a series of rhythms that recalls the relentless dynamism of life.”
Vernier is currently working in New York with the Juilliard School, researching the immateriality of sound and music and hoping to create a series of installations based on her findings. She is also collaborating with architect Jean Nouvel on the National Art Museum of China, based on the concept of shaping a building to imitate the energy, simplicity, and power of a single brush stroke. “My old masters would have been very proud,” she says.” [credit]
“Shiraga’s artistic legacy is rooted in post-war Japan when people were full of energy and there was excitement in the air pushing to try new things. This aspirational spirit, which reined in the society, led to the appearance of new art movements including one of the most famous and highly acclaimed groups, Gutai, of which Shiraga became one of the most renowned representatives.
Gutai Art Association, the first radical, post-war artistic group in Japan was founded in 1954 in Osaka under the leadership of Jiro Yoshihara. Yoshihara’s motto was simply to do what no one had done before and not to imitate others. The group’s artists that went on to great renown, like Saburo Murakami, Sadamasa Motonaga and, of course, Shiraga fully embraced the free spirit of the art and raw, concrete (Gutai in Japanese) creativity. However hardly anyone in the movement embodied Gutai’s philosophy more dramatically than Shiraga, who developed a unique technique of pouring paint on the canvas and creating brushstrokes with his feet by swinging on a rope hung from the ceiling.
Shiraga was born in Amagasaki, Hyogo Prefecture, in 1924 into the family of a kimono business owner. From early childhood due to his background he had access to the marvels of traditional Japanese art: calligraphy and antiques, classical theatre and cinema, ukiyo-e prints and ancient Chinese literature. After studying traditional Japanese painting in Kyoto, Shiraga fulfilled his long desire to explore Western paintings. He moved away from the figurative style and pursued a more emotional direction. As a result, in the early 1950s his work arrived at total abstraction following closely the mood of the times – to challenge conventional artistic forms. The Tokyo retrospective opens with a selection of Shiraga’s unfamiliar abstract works from this period dating as early as 1949 when the artist was only 25 years old.
Around 1952, Shiraga together with artists Murakami and Akira Kanayama formed the Zero Society (Zero-kai) relying on the idea that art should be created from the point of nothing. Shiraga started experimenting with fingers using them to make distinctive patterns, as shown in a couple of works on view. The finger technique eventually led him to placing the canvas flat to avoid the paint dripping. It made reaching the canvas center impossible unless the artist would step on it. And so he did. In summer 1954 the legendary Shiraga’s foot paintings (otherwise sometimes referred to as action paintings, the term originally coined for Jackson Pollock’s works) were born and the same year the artist joined the Gutai movement. The primordial energy of these new foot works explored tension as well as the sense of power. Sliding on the canvas Shiraga used his physical strength to reach a certain state between conscious and unconscious reducing his painting approach to a performance. It was a visual record, a memory of a specific action at a particular moment in time. Shiraga wouldn’t stop exploring the possibilities of a painting practice that would document his canvas exercises.” [credit]
[credit]
“Composer/performer Pamela Z will lead participants on a walk that creates musical scores from the graphic features (micro and macro) of downtown Manhattan. Participants will form a roving experimental sound and performance ensemble that will interpret and play the neighborhood’s building facades, sidewalk hardware, public art and street markings to make a contrapuntal, chance-based chorus.
This walk holds 12 people and is part of Urban Design Week 2011, organized by The Institute for Urban Design.
Click here to see photos from “Site Reading.””
“Pamela Z is a composer/performer and media artist who makes solo works combining a wide range of vocal techniques with electronic processing, samples, gesture activated MIDI controllers, and video. She has toured extensively throughout the US, Europe, and Japan. Her work has been presented at venues and exhibitions including Bang on a Can (NY), the Japan Interlink Festival, Other Minds (SF), the Venice Biennale, and the Dakar Biennale. She’s created installation works and has composed scores for dance, film, and new music chamber ensembles. Her numerous awards include a Guggenheim Fellowship, the Creative Capital Fund, the CalArts Alpert Award, The MAP Fund, the ASCAP Award, an Ars Electronica honorable mention, and the NEA/JUSFC Fellowship.Pamela’s website”
“The film combines men and women almost equally, capturing their exposed buttocks in a tight frame that results in quadrants of flesh, hence the “No. 4″ of the title. Since the telltale part of the human anatomy is facing away from the camera, the viewer is left to parse out identity based on subtle signs of difference, including hair, fat, and shape. Motion comes into play because the subjects are shot while walking, a fact that can be guessed by carefully watching the film and that is proved in a production still, which illustrates the simple rotating contraption on which they moved in place.”
Credit: Waxman, Lori. Keep Walking Intently: The Ambulatory Art of the Surrealists, the Situationist International, and Fluxus. Sternberg Press, 2017. Page 261.
[credit]
76 floor rubbings
made on the sidewalks of New York
18″ x 24″, graphite on paper, 2008
Edition of 3
There are seventy rubbings in the series and they were installed as a grid on the wall, with varying dimensions depending on the location. The simple act of tracing in this set of walking-based drawings asks questions about borders, public versus private space, and how people mark space.
—
“Francisca Benitez (b. 1974, Chile) lives and works in New York. Recent solo exhibitions include Cuchifritos Gallery + Project Space, New York (2014); Museo de Artes Visuales, Santiago, Chile (2013); Die Ecke, Santiago, Chile (2011); and Nada.Lokal, Vienna, Austria (2009). Notable group exhibitions include Mapping Brooklyn, Brooklyn Historical Society and BRIC House, Brooklyn (2015); Efemérides, Museo Histórico Nacional, Santiago, Chile (2014); Pier 54, High Line Art, New York (2014); One Minute Film Festival 2003 – 2012, MASS MoCA, North Adams, Massachusetts (2013); The Street Files, El Museo del Barrio, New York (2011); and Contaminaciones Contemporáneas, Museu de Arte Contemporánea da USP, Sao Paulo, Brazil (2010). Her work has been featured in major international exhibitions including the Bienal de la Habana, Cuba (2015); Lisbon Architecture Triennale, Portugal (2013) the Beijing Biennale, China (2009); and the LA Frewaves 10th biennial of film, video and new media, Los Angeles (2006).” (credit)

Eduardo Navarro – Poema Volcánico – 2014
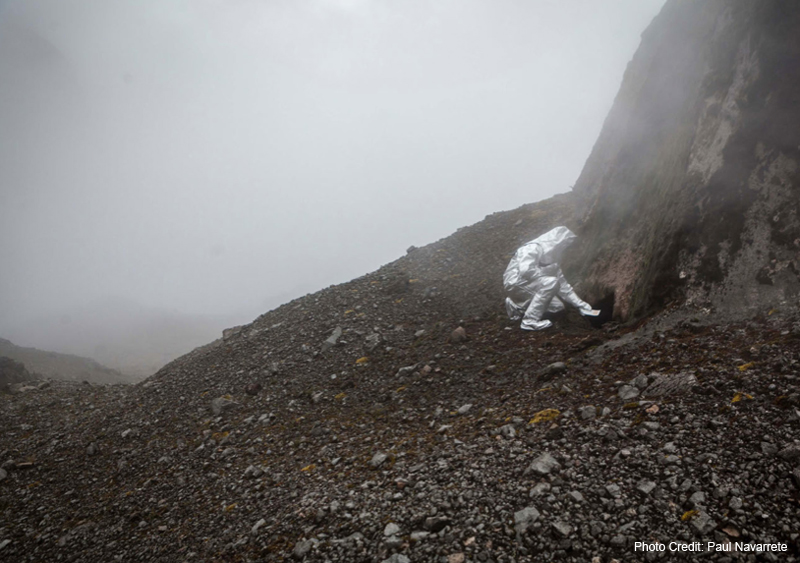
Poema Volcanico deals with the Ecuadorian volcanic geography. In 2014, while climbing the active volcano Guagua Pichincha, Eduardo Navarro created drawings from litmus paper, which measured the acidity of the gas emissions produced by the fumaroles inside the crater of the volcano. [credit]
“Eduardo Navarro lived in Ecuador between the ages of eight and twelve. During that time, Navarro would eat breakfast and dinner daily in front of a volcano, pondering it. The artist noted that as an adult, it meant a lot to him to return to the country to create a work of art that was both sentimental and a personal artistic challenge.
Leading up to the 12th Bienal de Cuenca, Navarro got the idea for his volcano-related artistic endeavor. He thought, “How can I work with the geography, landscape, and energy of the volcano?“ Instead of documenting a volcano (since we live in a world overly saturated with on-demand digital imagery), he wanted to create a project that would allow the volcano to express itself, and to do this, decided that he would have to enter it.
Navarro then got in contact with renowned Ecuadorian volcanologist Silvana Hidalgo of the Instituto Geofísico in Quito to confirm for certain which volcano it would be possible for him to enter without assuming the actual risk that it would erupt while he was inside. Through his extensive research and conversations with Silvana, Navarro decided to work with the Guagua Pichincha volcano.
Guagua Pichincha was known as one of the safer active volcanoes to trek into in Ecuador. To provide a comparison, Cotopaxi was another option, but Navarro explained that one had to be on the level of a professional mountain climber to enter its crater. Guagua Pichincha, on the other hand, was known in Ecuador as the “training mountain” that one would tackle before becoming a professional climber.” [credit]

Guagua Pichincha volcano
“Once Navarro decided upon the Guagua Pichincha, he had to figure out what his process would be leading up to the climb and artistic execution. After spending the required monthlong period adjusting to the proper oxygen level for the climb, Navarro decided to enter the crater twice, with two different guides (including record-setting climber Karl Egloff). His first trip would be to see what the crater was like, test expectations, and become familiar with the experience of going inside it. His second trip would be geared toward executing the artistic portion of the project.
On the first trip, Navarro realized first-hand how difficult it was to trek down into the crater and come back up, regardless of the intense physical prep work he made sure to do in advance. Also on the first trip, Navarro identified fumaroles (the cracks where smoke escapes from the volcano’s center) as the feature of the volcano he wanted to pursue working with artistically.
In regard to how he was going to work with fumaroles, one of Navarro’s first ideas was to get a woven basket, lower it down into the crater, and then try to pull it back up and see what would come out. Navarro thought that this could be an interesting idea, not only because baskets are accessible and would allow gases and sulfur to move freely through them, but because choosing woven baskets would give him the opportunity to work with an object that was native to Ecuador.
Navarro then had only a ten-day period between his two descents to figure out the details of both the device he was going to provide the volcano with so that it could express something, and the protective suit he was going to wear during the trek (most volcanologists wear fire protection and oxygen masks when entering craters). He went to the local fire department and asked if he could borrow a fireproof suit, and while the personnel there couldn’t provide him with one, they directed him to where he could get the materials so that he could make one of his own.
There is no question that Navarro’s descent into the crater was a high-risk undertaking. Navarro noted:
It is a sad thing when you pass the guards in the front (entrance) at Guagua Pichincha. A few weeks prior, three geologists went in. One almost died and two had to be rescued with a helicopter, so this was much more dangerous than going for a hike, having a picnic, taking a photograph, and climbing out.” [credit]

Eduardo Navarro – Poema Volcánico – 2014
“Returning to the execution of his artistic endeavor, Navarro revisited the Instituto Geofísico to speak further with Silvana, who was crucial in the process. When Navarro raised the question, “How can I make the volcano draw?,” Silvana suggested the possibility of using litmus paper to react to the sulfur. Navarro immediately loved this idea, and started working with using litmus paper to create a machine that would allow the volcano’s energy to leave a trail. The result was a hand-made frame that acted as a rack for the sheets of litmus paper, which fit inside a custom woven basket that he worked closely with local artisans to create. Navarro wore the basket like a backpack during his trek, and eventually lowered it into the fumarole. He then left it down there for one hour, providing the volcano with a chance to leave its mark and express itself as if typing on a PH-reactive typewriter (example of result featured below – top right).
Ultimately Navarro titled this work Poema Volcánico because of the act of “handing the typewriter” over to the volcano. In other words, Navarro gave the volcano the power to express something that was not his interpretation of it.
To expand, it can be argued that Navarro gave true authorship to the volcano because he wasn’t attempting to control the project’s result. In fact, throughout the entire process, there was always the chance that the volcano and litmus paper wouldn’t have any real reaction at all. Even after months of preparation and two rigorous climbs, Navarro admitted that he was willing to accept any outcome. For Navarro, “it would have been fine if the volcano didn’t have anything to say.”
Setting himself apart from the many other talented artists who have been inspired by volcanoes throughout the centuries, Navarro’s intention was to transform the volcano from subject into artistic collaborator. Navarro does not claim that the volcano is necessarily the author of this work, nor that he himself is the author of this work. To Navarro, Poema Volcánico is about how well he and the volcano know each other.” [credit]

Eduardo Navarro – Poema Volcanico 2014

Brendan Stuart Burns, Artist’s Journal

[credit]
“Brendan Stuart Burns’s paintings, drawings and photographs are a direct and physical response to both his walks and his more contemplative moments experienced along particular stretches of the Pembrokeshire coast which he has come to know intimately. Time spent walking, often over the same stretches of the same beaches in all weathers and states of the tide, provides him with the experiences necessary to touch and connect physically and emotionally with the land, its history and deep sense of time, all elements that are ever present in his paintings.
His works present simultaneously a ‘direct’ and ‘sensed’ experience of the landscape, its geology and geomorphology, in addition to the complex psychological effects such places have on the individual. Horizons shift and scale becomes relative as both close-up details and wider perspectives are referenced, often within the same pieces of work, and recreated later in the studio from copious notes and sketch books. Fundamental to Burns’s method is his layered use of oil and wax, building and constructing an equivalent to the experience of surface, form and space.
Each work accordingly sits on the edge between abstraction and representation, reflecting the uneasy balance between the physical and the psychological, intention and accident, the intuitive and the considered. They recreate the entirety of Burns’s experience for us (the transformation of daily and annual cycles; changing climatic and tidal conditions), rather than merely documenting a discrete moment within the traditional confines of naturalism.”