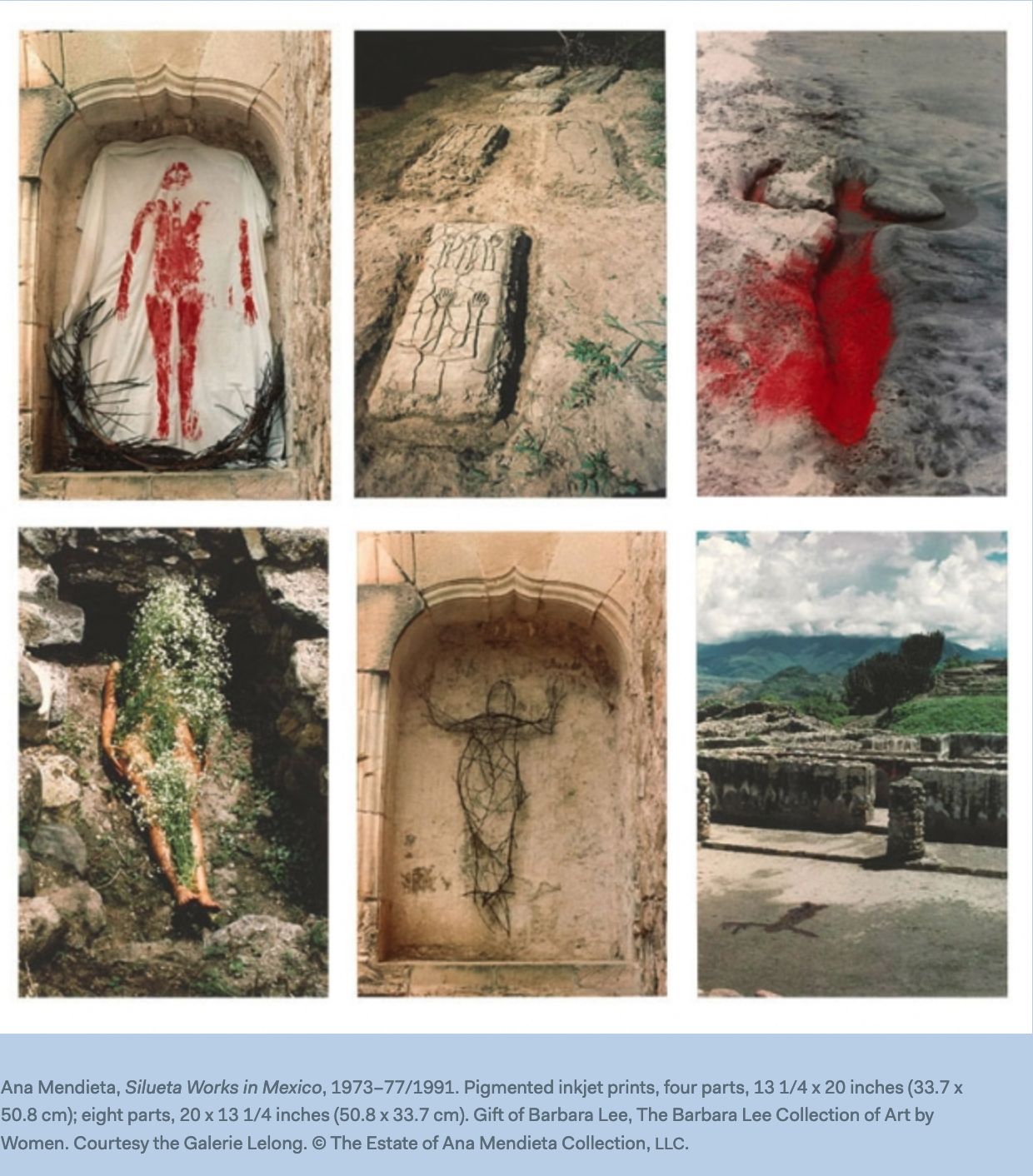
“The “Siluetas” comprise more than 200 earth-body works that saw the artist burn, carve, and mold her silhouette into the landscapes of Iowa and Mexico. The sculptures made tangible Mendieta’s belief of the earth as goddess, rooted in Afro-Cuban Santería and the indigenous Taíno practices of her homeland. Exiled from Cuba at a young age, Mendieta said that she was “overwhelmed by the feeling of having been cast from the womb (nature).” Seeking a way to, in her words, “return to the maternal source,” she used her body to commune with sand, ice, and mud, among other natural media, as a way to “become one with the earth.”
Yet these works resist easy categorization in form or theme. The “Siluetas” are not self-portraits or performance pieces, except perhaps to the few who witnessed them. Each piece was subsumed by the earth, meaning photographs are the only remaining traces. Similarly, the thematic complexity of Mendieta’s life and these sculptures resist collapsing into neat categories of nation, diaspora, race, or gender. By using the body as both an image and medium, these aspects of identity are complicated. Mendieta’s earthworks occupy a liminal space between presence and absence, balancing the inevitable politicization of the self while searching for meaning in older, sacred traditions. …
The “Siluetas” were an ongoing, ritualistic relationship between Mendieta and the land. I read each work as a spell, a fragment of an ongoing incantation that was not “the final stage of a ritual but a way and a means of asserting my emotional ties with nature,” as Mendieta once said. She wanted to send “an image made out of smoke into the atmosphere,” so that each work was designed to disappear, to be reclaimed by the force she revered in an effort to come closer to it.” [credit]
“Spanning performance, sculpture, film, and drawing, Ana Mendieta‘s work revolves around the body, nature, and the spiritual connections between them. A Cuban exile, Mendieta came to the United States in 1961, leaving much of her family behind—a traumatic cultural separation that had a huge impact on her art. Her earliest performances, made while studying at the University of Iowa, involved manipulations to her body, often in violent contexts, such as restaged rape or murder scenes. In 1973 she began to visit pre-Columbian sites in Mexico to learn more about native Central American and Caribbean religions. During this time the natural landscape took on increasing importance in her work, invoking a spirit of renewal inspired by nature and the archetype of the feminine.1. Ana Mendieta, quoted in Petra Barreras del Rio and John Perrault, Ana Mendieta: A Retrospective, exh. cat. (New York: New Museum of Contemporary Art, 1988), p. 10.
2. Ana Mendieta, “A Selection of Statements and Notes,” Sulfur (Ypsilanti, Mich.) no. 22 (1988), p. 70.” [credit]